
GSM termination (aka. Call termination) – is a merge of Internet networks and mobile networks. Simply put, Internet network is called VoIP (voice over Internet protocol) and mobile network is called GSM.
But how to merge Internet networks and mobile networks?
There is a special equipment for Call Termination which is called VoIP gateway. Different types of networks are connected by means of this VoIP gateways. And it is an affordable purchase for any person. Exactly this device assists in joining very profitable GSM Termination business.
So how does mobile network function?
When we want to call somebody, we dial the number. Then our voice traffic is sent to mobile operator, which, in its turn, uses transit operator with the best route to deliver this call to final subscriber, and pays certain amount of money to transit operator for the delivery of call. A mobile operator is physically restricted to deliver a call between continents or countries because of: geography, political situation, technological and commercial causes. That is why several transit operators are involved in call delivery while these networks are involved in the transfer of the call. With the help of these networks transit operators cooperate with each other. Therefore, via gateways transit operators help the operators with different types of networks and with their subscribers connect with each other. That is why transit operators do not have their own subscribers, they provide telephony services to other operators that have their own subscribers.
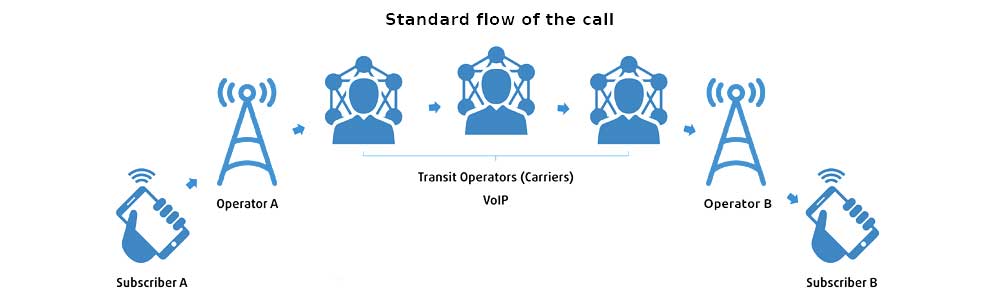
What does the transit operator do next?
Transit operator is buying route from GSM terminators (usual people who have VoIP gateways).
GSM terminators are a category of operators, who are our customers in purchasing ANTRAX equipment and Flames Group partners for providing of voice traffic. GSM terminators are providers of direct alternative routes for transit operators such as our company.
- GSM terminators have no subscriber base.
- GSM terminators cooperate with small transit operators.
- Voice traffic (calls) from transit operators passes through the GSM terminator equipment.
It is advantageous for national operators to cooperate with transit operators, which have many routes and a lot of capacity. Transit operators cooperate with operators with their subscriber base and with other transit operators. Transit operators realize that the cheaper they buy the route for the transit of voice traffic, the more money they will earn.Therefore, transit operators are looking for alternative routes and cooperating with small transit operators (Flames Group is just a small transit operator). Small transit operators in turn aggregate (collect) GSM terminators.
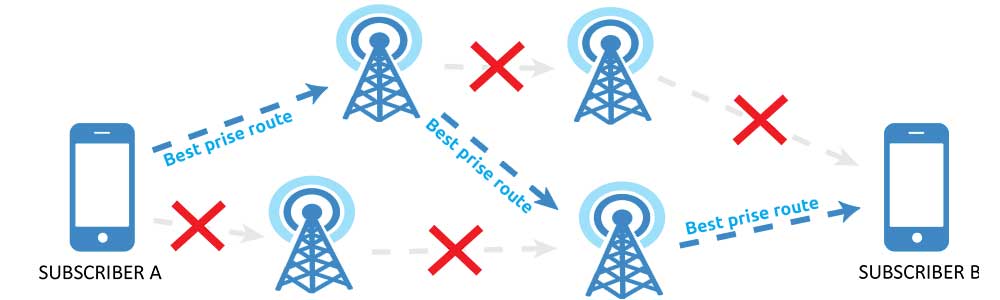
As this is the business based on profit from international voice traffic. Difference between local call cost and international call cost will be a profit.
What is VoIP/GSM gateway?
This is a device that carries the voice traffic from the Internet network to the mobile operator’s network. This is a unique solution for high-quality termination of voice traffic, which helps significantly reduce the cost of international calls, equating them to the cost of local calls.
This Software and Hardware Complex consists of two different parts:
-
First important part is GSM gateway. What does it do? In fact, it is just a box which contains GSM modules which sends signals from the Internet. It consists of up to 4 or 8 GSM channels. That is 4 or 8 simultaneous calls.

ANTRAX gateways support all band of GSM frequencies, GPRS and IMEI change. -
And second required part of this complex is a SIM Box – the place where the SIM cards are stored. SIM Box allows you to install and manage any amount of SIM cards of different mobile operators that enables work of several GSM gateways placed in different locations. Available configurations: 60 sims and 120 sims.
Several SIM Boxes can be consolidated in one system that provides with a possibility to use unlimited number of sims in your system.
But how to use it and how you can get route?
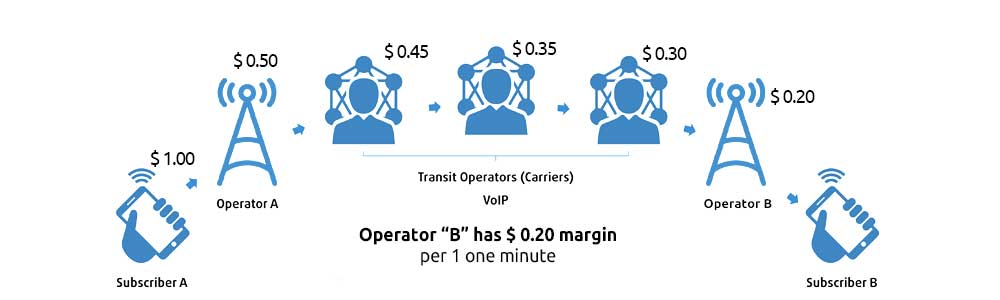
There is a mobile operator by means of which you call. Your call goes to your mobile operator. Then the call goes to the transit operator A through another transit operator B. And through another transit operator C and gets to the mobile operator which subscriber you are dialing.
For example, you pay 20 cents for a call. Your mobile operator pays a transit operator A – 15 cents. Then the transit operator A sells the call to another transit operator B for 12 cents. Therefore, the transit operator B sells the call to another transit operator C for 8 cents. So, the difference between these amounts is the margin. That is, the mobile operator’s profit is 5 cents. The profit of the transit operator A is 3 cents, the transit operator B – 4 cents and so on. The margin is your profit.
Hundreds of thousands of calls are made every day by means of this method. And you understand that each of these mobile and transit operators receives a huge income.
How can we get into this financial flow with the help of a VoIP/GSM gateway?
The call goes to the mobile operator. Further through all the transit operators. And it does not come to the mobile operator of the country where the call is being delivered, but goes to your VoIP/GSM gateway. And your gateway redirects the call to the person dialed by the subscriber.
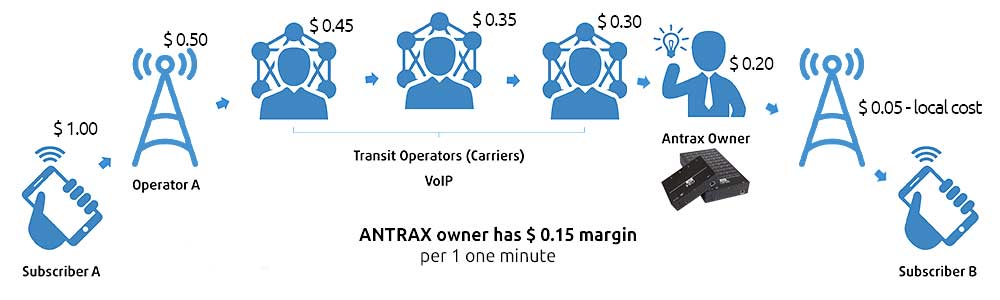
And you get money for delivering a call instead of a local mobile operator. It should be noted that your profit depends on the quality of your route and on the capacity of your route
What is the quality of the route?
There are such indicators as:
- ACD (average cell duration). If your average call duration is 3-4 minutes this is a very good indicator.
- ASR (Answer Seizure ratio). If this ratio is equal to 30-50% this is considered as a good indicator.
- Capacity is the number of channels which your route passes through. If your route has 30 channels, then it will skip 30 calls at the same time. The more channels the greater the profit.
CLI – Calling line identification. Not supported
GSM terminator payment options (every two weeks):
- Money transfers: Western union, Union pay;
- The bank account to which the card is attached – visa or master card ( USD only);
- Electronic money, for example, webmoney. These systems are international and, as a rule, do not fall under the monitoring of states.
- Creation of an offshore company and opening an account abroad. A very popular offshore territory is Panama, Hong Kong, Georgia, countries in Asia, Middle East. But in civilized countries, companies that are registered in offshore zones cannot be paid. There is a black list of zones where it is extremely undesirable to send international payments. The account can be opened in any other country, in Europe, for example, it is popular to keep money in Switzerland, for the CIS countries it is Latvia.
Flames Group – a European company, pays all taxes and keeps being audited.
